- Author Matthew Elmers elmers@military-review.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 21:49.
- Last modified 2025-01-24 09:17.
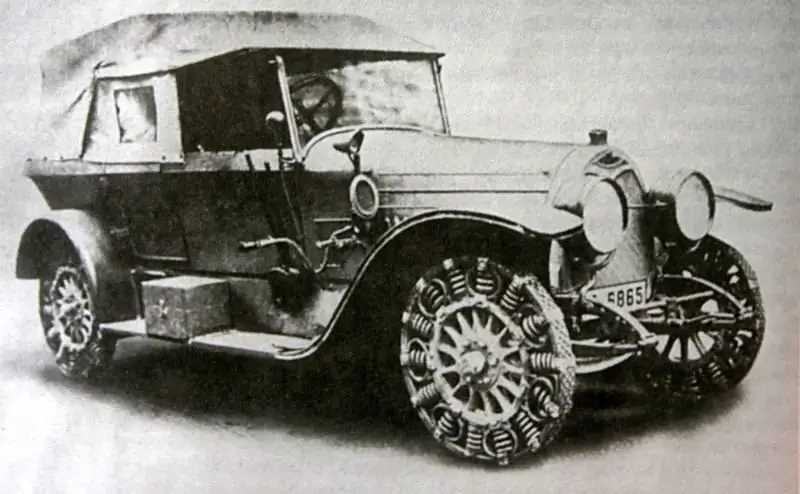

The general appearance of a car wheel with a central disc and a tire filled with air was formed a long time ago and confirmed its effectiveness. However, attempts are regularly made to radically rebuild such a structure in order to improve its technical or economic characteristics. A certain popularity in this context is enjoyed by the so-called. airless tire with elastic elements and without compressed gas..
Long story
The first variants of airless tires appeared almost at the beginning of the last century. Often the reason for the emergence of such projects was a shortage of materials. Designers tried to replace hard-to-reach and expensive rubber with more profitable wood or metal. To date, the shortage problem has been resolved, and new projects are associated only with the desire to improve the characteristics of the chassis.
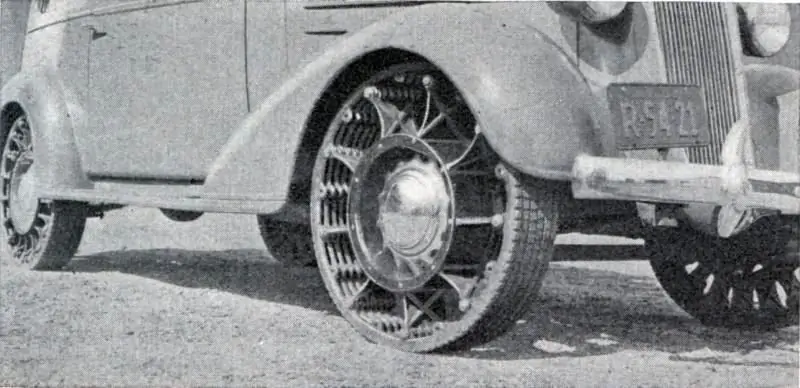
Early airless tire designs most often offered a metal rim and outer rim with tread, connected by a set of springs of various shapes and configurations. At various times, coil or leaf springs were used. Such designs generally solved the assigned tasks, but turned out to be too complex and inconvenient to operate. As a result, they did not go into a large series and did not receive wide distribution.
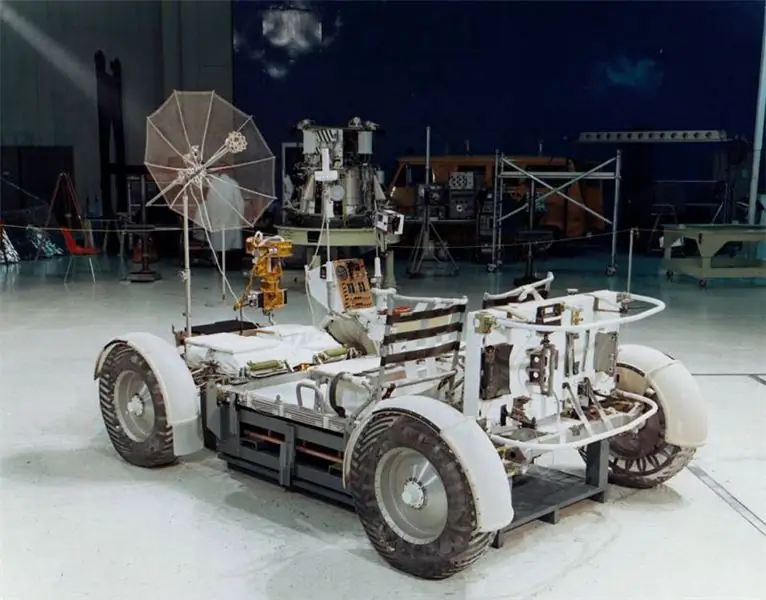
Relative success came to airless tires only with the development of space programs. It turned out that rovers of the type of the Soviet "Lunokhod" or the American LRV should be equipped with wheels without cameras and air. So, the LRV product from the Apollo system received an elastic tire made of metal mesh with a riveted tread. This design was light, dampened shocks, did not require maintenance and was distinguished by high survivability.
Some of the designs of airless tires at various stages attracted the attention of the military and even reached field tests. In recent years, there has been renewed interest in such developments, and this is not only about projects for the armies. Leading tire manufacturers are looking at airless construction as a viable alternative to traditional wheels.
However, until now, none of the known models have reached mass production and operation in the military or civilian sphere. The undercarriage revolution is hampered by objective factors.
Contemporary designs
Consider some of the modern airless tire designs developed in recent decades. So, in the past, the Airless project: Resilient NPT by Resilient Technologies was widely known. It has been in development since 2002 and reached testing at the end of the decade. Using modern polymer materials that were not available in the distant past, American engineers were able to create a very interesting design.
Airless Tire: Resilient NPT is a one-piece design that includes a center disc for mounting, an outer rim with tread, and a special cage in between. The latter is made in the form of a lattice structure of irregular hexagons and trapezoids. The weight of the car is distributed between the relatively rigid rim and grille. At the same time, the elasticity of the structure allows you to damp shocks.
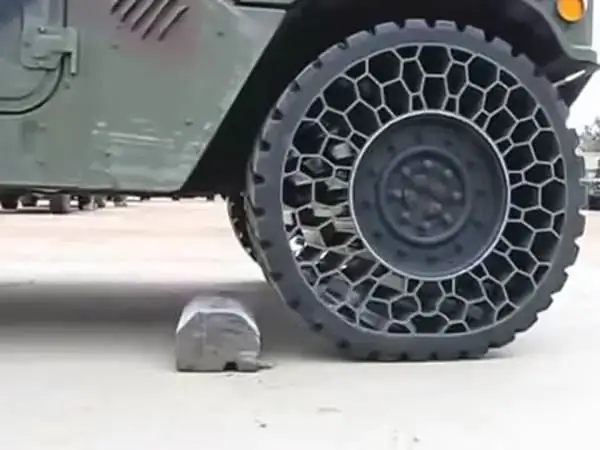
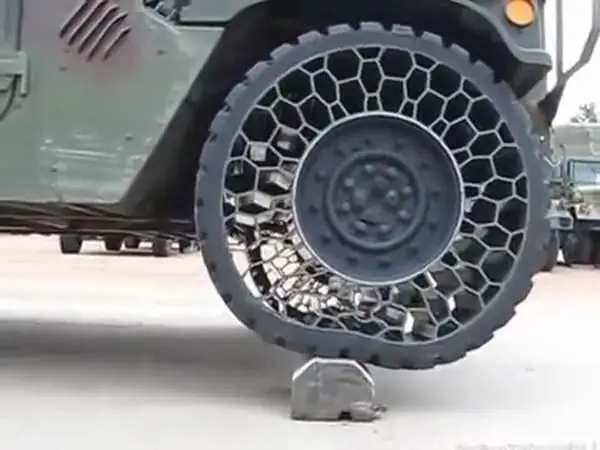


Tests have shown that the Airless: Resilient NPT tire is comparable in damping to a traditional pneumatic tire. It is not afraid of punctures and can be used when 30% of the frame elements are damaged. There was also a small gain in mass. Nevertheless, the product was quite difficult to manufacture, required special materials and had a number of other disadvantages. As a result, tires from Resilient Technologies have not yet entered the army.
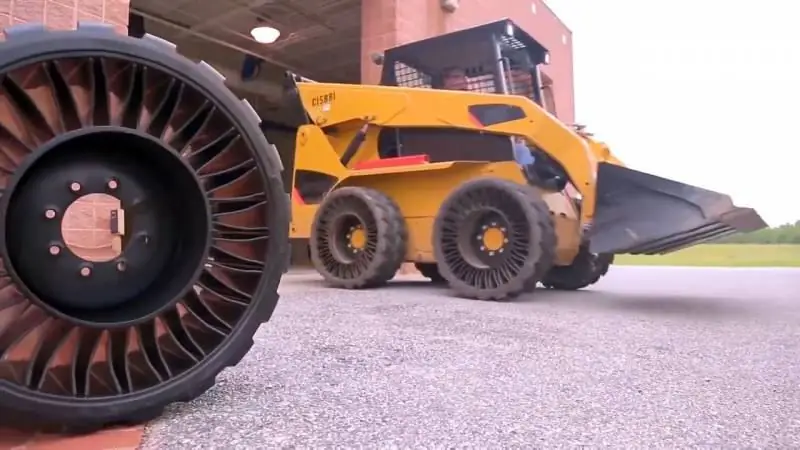
In 2005, Michelin introduced the Tweel (Tire + Wheel) concept tire. In this design, the center disc and outer rim are connected by V-shaped "spokes" that run the entire width of the tire. The developer talked about reducing weight in comparison with traditional products, increasing resource, etc.
After testing and development, the Tweel tire was developed. There are modifications of this product for vehicles of different classes. In 2012, the supply of such tires for construction and agricultural machinery began. Later, new models of such products with a different configuration of elastic elements appeared.

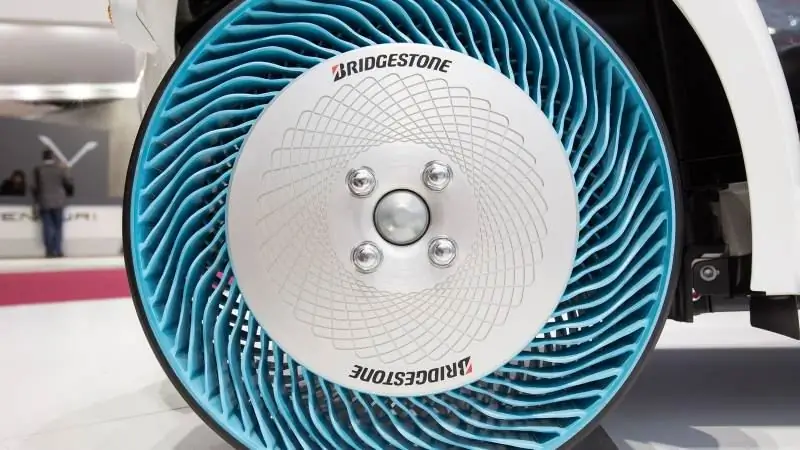
Bridgestone also has its own version of the airless tire. She suggests connecting the disc and the rim with curved "spokes" located crosswise. This cushioning made it possible to increase the elasticity while maintaining other characteristics. However, the finished samples had a limited carrying capacity, which reduced the scope of application.
There are other variants of airless tires of various kinds that have come down to testing or even to production. The search for new solutions continues. Designers try different materials, elastic configurations, etc. However, there have been only limited successes.
Advantages and disadvantages
The airless tire with integrated resilient elements has several important advantages over the traditional pneumatic tire. It is they that determine the increased interest in such designs, which has been observed so far.
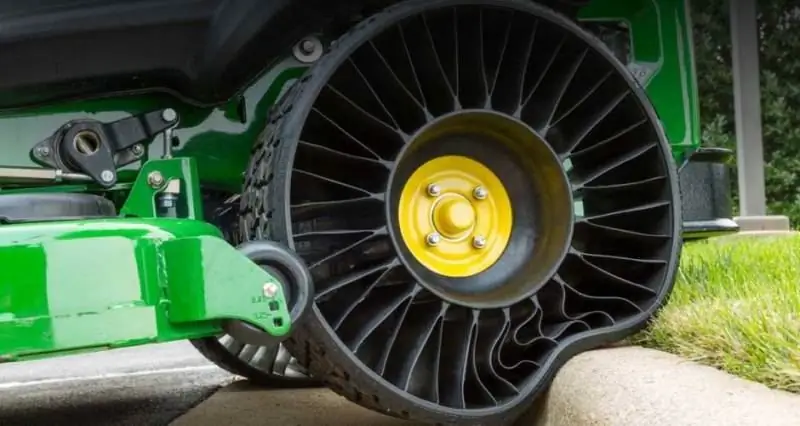

The main plus is increased survivability. An airless tire has no air chamber and is puncture-proof. She is also not afraid of side impacts. Depending on the architecture, performance is maintained even in the event of severe damage to the supporting structure. There is no need for pumping and pressure monitoring, which simplifies operation. There is a possibility of abandoning a large and relatively heavy wheel rim. As a result, the wheel assembly is lighter, which reduces the unsprung mass.
However, there are a number of problems due to which such tires do not gain popularity. First of all, this is an increased demand for materials. Requires rubber or polymer with sufficient elasticity, high rigidity and strength to various loads. There are also high requirements for the absorption of mechanical energy and its transformation into thermal energy with subsequent dissipation.
All this complicates and increases the cost of production. In addition, most tires have a speed limit - usually no more than 70-80 km / h. Further acceleration increases mechanical stress and also leads to unacceptable overheating.
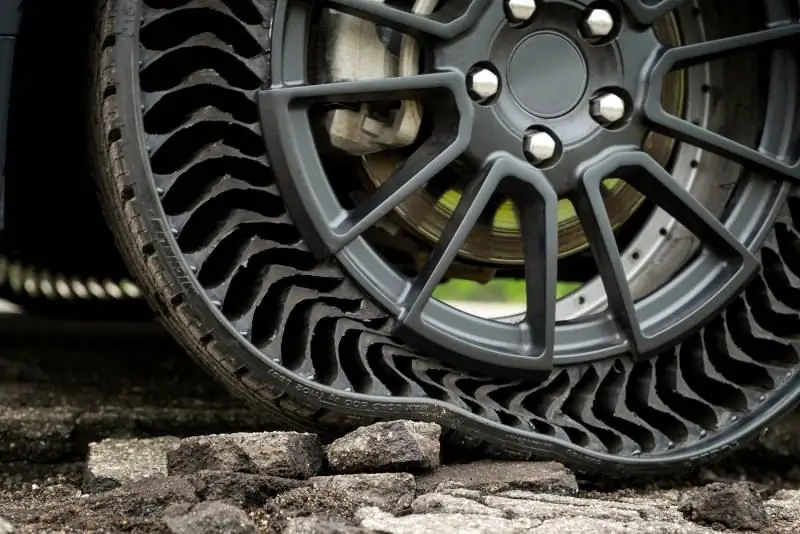

Unlike pneumatic tires, airless tires have a constant stiffness, and you need to change the wheels to change it. At the same time, the ingress of dirt into the structure through the open sidewalls can negatively affect the rigidity and other characteristics. From these points of view, pneumatic structures are much more profitable.
As a result, airless tires are still used mainly in the field of light vehicles with limited speeds and loads. They are put on golf carts, some buggies, compact construction equipment, etc. Also, the production of tires for bicycles, scooters and other light products has been established. The provision of larger samples is still in question.
A promising curiosity
The specific combination of technical, operational and economic characteristics, as well as a number of significant limitations, do not yet allow airless tires to enter the wide market and seriously compete with traditional designs. As a result, the tire market does not change - although different firms regularly present various “promising” products.

However, it should be noted that individual products of the original design nevertheless entered the market and even found their customers. Success is observed in several rather narrow niches, while the conquest of the main sectors of the market turns out to be impossible. There are no objective prerequisites for a change in this situation.
Thus, various variants of airless tires with integrated elastic elements in general retain the status of a curious solution to an important technical problem - without particular prospects in the context of real application.
On the other hand, such projects can have positive results that are not directly related to the use of finished products. Recognized industry leaders with a good scientific and technical base are now engaged in the development of such tires. In the course of developing airless tires, new materials, technologies and designs can be created. And they can find application in the development and improvement of traditional tires with real practical and commercial prospects.






