- Author Matthew Elmers elmers@military-review.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 21:49.
- Last modified 2025-01-24 09:17.
Israel began developing its own tank in 1972, and in 1977 the first photographs of prototypes of the Merkava tank were presented to the press. The first public display of the tank took place in 1979 on the Israeli independence day. The specificity of Israel and special design ideas led to the creation of a rather unusual main battle tank, which has a number of interesting features.
Features of Israeli tank building
It may seem strange, but the main restrictions on the weight and dimensions of the tanks are imposed by the railway transportation standards. Tank units must be quickly moved over long distances, MBT should not create problems for railway platforms, pass under bridges and tunnels. In Israel, initially they expected to use the tank only on its compact territory and carry out transportation using special auto platforms. Dimensions and weight did not weigh on the designers, so the "Merkava" is today one of the heaviest tanks in the world. The mass of the Merkava Mk4 modification reaches 65 tons, a number of sources indicate a value of 70 tons.
The features of the proposed theater of hostilities set the narrowness of the geographic and climatic capabilities of the tank. "Merkava" is not intended for operations in cold winter conditions, off-road mid-lane, tropical humidity, swamps. Its elements are gentle mountains, dry desert and subtropics, which reduced the export potential of the car to a minimum.
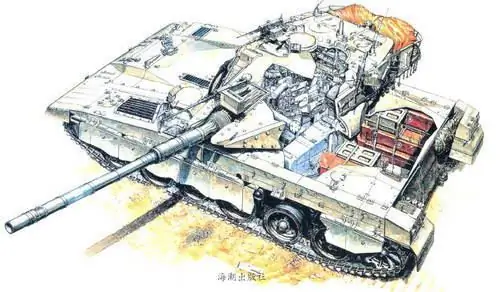
The design was also influenced by the fact that the Israelis prefer to conduct defensive actions from positions located on the slopes of heights. Based on this method of firing, a high probability of shells hitting the tank turret was assumed. That is why the designers tried to move the fighting compartment from the turret to the hull as much as possible and reduce its frontal silhouette.
Another factor was the increased concern for the survival of the crew of the combat vehicle. The crew was positioned slightly lower and behind than most modern tanks. The engine and transmission are installed in front of the tank, which are protected by a heavy cast armor plate, on the inside of which, at some distance, a second armor plate 60 mm thick is installed. The cavity between them is occupied by a fuel tank. Another 20 mm thick armor plate is mounted behind the engine. Thanks to this, the tank's crew was provided with serious protection from frontal hits.
During the development of the tank, much attention was paid to the issue of the comfortable work of tankers. The designers, in fact, proceeded from the concept that the tank is the home of the crew during the war. In particular, a very controversial concept of round-the-clock use of the tank was proposed, for which it was supposed to place 2 crews in it - one is at war, the other is resting. If necessary, the places of the reserve crew could be taken by the wounded. This concept led to the creation of an unprecedented hull volume in modern world tank building, which in turn was reflected in the size of the tank. The possibility of transporting people inside the MBT puzzled a number of experts, some of them at one time even tried to single out the "Merkava" as a separate subspecies of BMP tanks. The fighting compartment of the tank can be used to transport servicemen and their property, and also allows you to evacuate the wounded from the battlefield. In the aft armor plate there is a 600 mm wide hatch that opens access to the fighting compartment.

Merkava Mk1
To date, 4 modifications of this tank are known. The very first "Merkava Mk1" is no longer in service with the Israeli army. The main tanks of the Israel Defense Forces are the Mk2, Mk3 and Mk4 modifications, respectively. The first models of the Mk1 and Mk2 tanks were armed with a 105-mm American M68 cannon, had less powerful engines with a capacity of only 900 hp, a simpler control system, and, as shown by the hostilities in which they had a chance to take part, insufficient booking. In the process of modernizing the tank, Israeli specialists took the path of building up all the above parameters and getting rid of the revealed childhood diseases. Consider the most modern models Mk3 and Mk4.
Merkava Mk3
According to British experts, the Merkava Mk3 was almost a new tank, not a modernized Mk2. As before, the key issue for the Israelis was to strengthen the protection of the combat vehicle. On MBT "Merkava Mk3" modular armor was used. Modules - special armor blocks - were bolted to the hull and turret of the tank. They have strengthened almost all the vulnerabilities of the car. The side skirts received more advanced armor. Unlike the West German Leopard-2 or the Soviet T-80U, in which the reinforced armor of the side screens is located only in the driver's area, on the Merkava the projectile resistance of the side screens is the same along the entire length of the hull. The turret of the tank is covered with modular armor from above and from the sides.
One of the advantages of using modular armor is the ability to quickly replace the damaged elements even in the field. Regarding the use of modular armor, Israeli General Israel Tal noted that this tank will always be forever young, it will not age, its armor can always be replaced with a newer and more advanced one. Particular attention was paid to the all-aspect protection of the vehicle, which was carried out taking into account the fighting in Lebanon in 1982. The protection of the tank from the stern was increased by installing armored fuel tanks in the stern armor plate instead of battery compartments and FVU (ventilation and filtration unit). At the same time, the batteries were moved to the sponson fenders, and the filter ventilation unit to the aft niche of the tank turret.

Merkava Mk2
As the main weapon, a 120-mm cannon was installed on the tank, which significantly increased its firepower. This gun is in many ways similar to the German Rh-120 and the American M-256, while the barrel rollback system on the Israeli gun is more compact. Shooting from this gun is possible with all types of ammunition of German and American production. The gun ammunition consists of 48 rounds. The barrel of the gun has a heat-insulating casing, and an ejector is mounted in its middle part, which serves to remove the powder gases. Its dismantling does not require the removal of the thermal insulation casing, and the replacement of the gun barrel is carried out without dismantling the turret.
Tank rounds are stored in individual containers for greater reliability. Five shots are immediately ready for battle and are located on the rotating turret floor. The magazine and the semi-automatic system for supplying ammunition to the gun is part of the AZ being developed. Now the loader loads the magazine with ammunition from individual containers. The shots are raised using a foot drive, after which the loader manually sends them to the breech. The Israelis believe that such a scheme allows a compromise between a relatively simple loading mechanism, which makes the gunner's work easier and increases the rate of fire, and the military's requirement for a tank crew of 4 people.
The tank had an improved fire control system manufactured by Elbit. The gunner received a new sight with the ability to automatically track the target, with an axis stabilization independent of the position of the gun barrel, with a 12x magnification and a laser rangefinder. The night channel of the gunner's sight has a 5x magnification. The commander also received a stabilized periscope sight with a 14-4x magnification and an independent night channel. The tank commander's sight is connected to the gunner's sight by an optical channel and allows the commander to carry out target designation. The electro-hydraulic drives for aiming the gun and turning the turret were completely replaced with electric ones to improve safety.

Merkava Mk3
For the first time in the history of Western tank building, a tank received an electromagnetic radiation warning system. 2 wide-angle sensors are installed on the sides of the rear of the turret, one above the gun barrel. All 3 sensors provide a circular girth, transmitting information about the azimuth of the radiation source to a small display located next to the commander's workplace.
The more powerful forced AVDS-1790-9AR engine - 1200 hp was responsible for the mobility of the tank. (the Mk1 and Mk2 models had 900 hp engines) and an improved hydromechanical transmission. The use of such an engine allowed the 63-ton car to accelerate on the highway to 60 km / h. The first tanks of this model began to enter service with the Israeli army in the early 1990s, the cost of one tank was $ 2.3 million.
Merkava Mk4
The new Israeli MBT Merkava Mk4 was first shown to the public in 2002. In 2004, the army received the first battalion equipped with these tanks. The configuration of the turret armor modules was significantly redesigned on the tank, and the tank gun received a mask. The armor of the turret roof has been significantly increased, which now covers the entire roof, and not just the front part of it. As a result of these measures, the loader lost the hatch, only the commander's hatch remained on the roof. The mass of the tank reached 65 tons.
In order to maintain mobility, a 12-cylinder water-cooled diesel engine (all previous ones were air-cooled) with a capacity of 1500 hp was installed on the tank for the first time. The components of this diesel engine are manufactured by the German company MTU, then assembled in the USA under license by General Dynamics Land Systems and exported to Israel under the name of the GD 883 power plant. The engine is mounted in a single unit with a 5-speed automatic transmission Renk RK 325.

Merkava Mk4
An improved 120-mm gun was installed on the tank, designed for increased pressure of powder gases. Together with the gun, a new, improved electric drum mechanism is now working, supplying shells to the loader and designed for 10 shells, the rest, as before, are stored in refractory individual containers in the rear of the tank.
The tank's control system has been improved. In particular, the thermal imaging channel, the automatic target tracking device and the panoramic sight of the tank commander were further developed. A video camera was placed in the aft part of the tank, which helps the driver navigate when reversing.
For the first time in the history of western tank building, the Merkava Mk4 received a complex of active protection against anti-tank missiles - Trophy. The complex operates in automatic mode and tracks targets in the 360-degree sector. At a distance of several tens of meters, 4 radars mounted along the perimeter of the tower detect anti-tank ammunition and give the command to destroy it. The estimated cost of the tank is $ 3, 7 million, the estimated cost of the Trophy active protection complex is no more than 10% of its cost.






