- Author Matthew Elmers elmers@military-review.com.
- Public 2023-12-16 21:49.
- Last modified 2025-01-24 09:17.
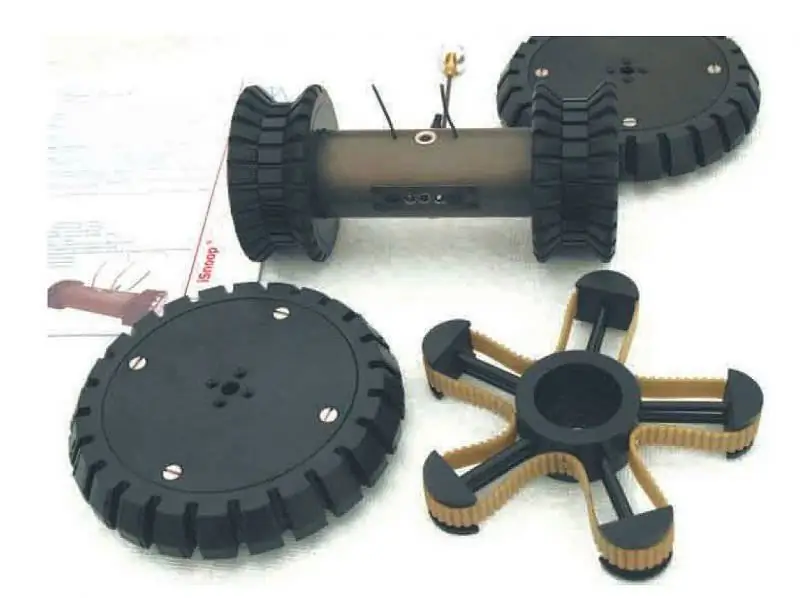

The German company Optimess developed the two-wheeled iSnoop, which was equipped with two types of wheels, one of which was designed to move up stairs.
Optimess: The German company Optimess has developed a new product iSnoop in the field of throwing robots. It is available with different wheel sets to achieve optimal mobility on different surfaces (including steps) and required speeds. Its wireless communication system provides an indoor range of 50 meters and an outdoor range of 200 meters.
A high-resolution panning camera captures video images and a microphone collects acoustic data. In addition to the standard chamber, other devices can be installed, for example, gas analyzers. iSnoop can run continuously for up to two hours, the robot is in its final stages of development and will be available in 2014.
Robo-team: A couple of years ago, the Israeli company Robo-team showed a lightweight, throwable robot with a cute acronym Iris, meaning Individual Reconnaissance and Intelligence System). It weighed one kilogram with two AA batteries that provided 4-6 hours of runtime; the launch was carried out using a sling-type throwing system. Over time, Iris has evolved into a pre-production product.
The robot was originally very robust, was made of composite materials and designed according to the "safe" concept, which allows it to withstand falls from a height of 10 meters or landings after flying 65 meters, making it possibly the robot with the "farthest throwability" … It was equipped with a frontal day / night camera with a ± 90 ° tilt mechanism, a visible and near infrared laser pointer and a microphone and a secure communication channel for 200 meters. Thanks to its symmetrical design, it could fall on either side and then be ready to go. The dimensions 175x205x95 mm allowed the soldier to carry the Iris in his pocket. The robot had an unusual design, the front axle was much wider than the rear axle. The wheels were made of composite nylon, each with six studs for hanging traction on hard ground.
During the second stage of development, most of the elements were retained, including the architecture. The concept of the sling was, however, dropped, although the Iris robot retained its throwing capabilities. The size has changed by 229x203x94 mm, the mass has grown to 1.3 kg, but the payload of one kilogram has been added. The wheels have also been modified. Several Iris robots in this configuration were supplied to customers who used them for testing and operation, giving Robo-team invaluable data for the development of the production version, which was first delivered in June 2014. The asymmetric architecture of the proven concept has been abandoned in favor of the traditional rectangular shape. The Picatinny rail on the upper platform can accept devices that are connected via the RS232 connector, video / audio or Ethernet connectors, of course, after installing them, there is no question of throwing the robot. The Iris robot is equipped with completely new wheels, it retains the ability to climb stairs and according to the Robo-team, its capabilities have increased compared to the first models. It can overcome obstacles with a height of 64 mm and slopes of 45 ° (100% in transport terms) and has a top speed of 4.8 km / h. The data transmission system has the ability to self-repair, expanding the range of the robot, especially in urban areas. The Iris is controlled by a Rocu-5 unit, which has been modified with the robot to offer a sunlight readable, resistive touchscreen compatible with 5 "night vision goggles instead of the previous 4.3" touchscreen. One finger stick was retained, and the number of buttons was increased to six, three on each side of the screen. The storage capacity has been significantly increased, adding GPS, accelerometers and a digital compass, as well as 5 MB front and rear cameras. The continuous operation time is 3 to 6 hours, but more importantly, the weight has been reduced from 700 to 540 grams.
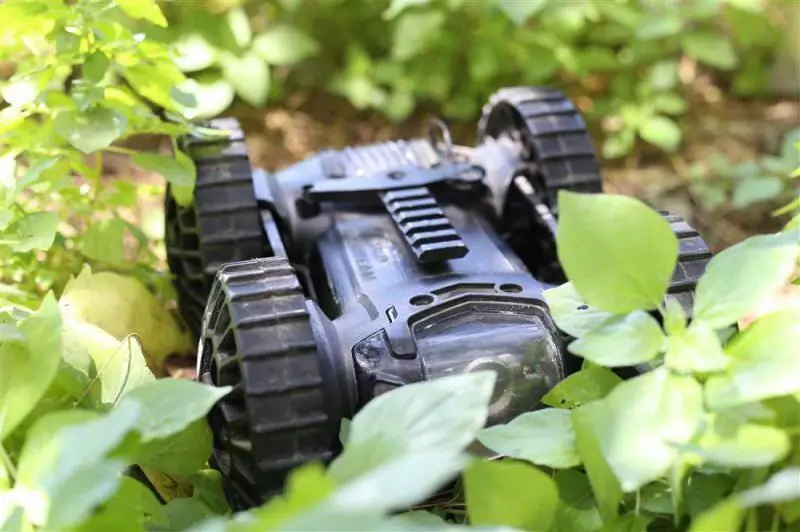


Robo-team's latest version of the Iris features a fully symmetrical design and features a Picatinny rail to accommodate devices weighing up to one kilogram
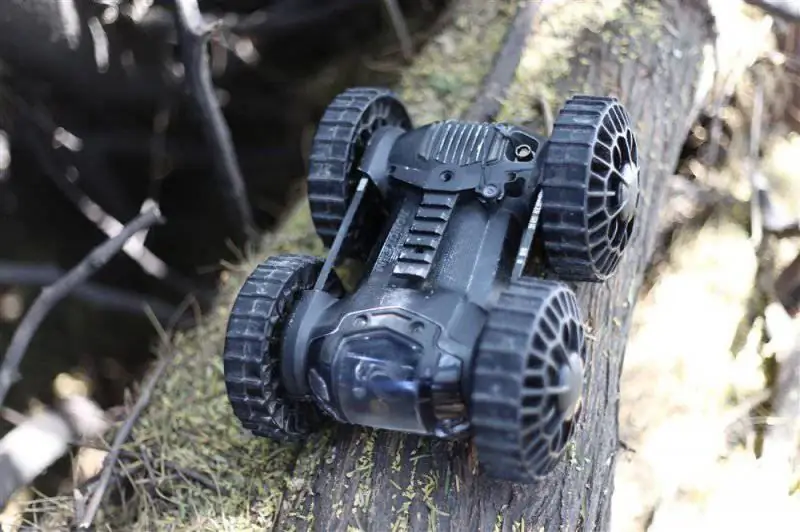
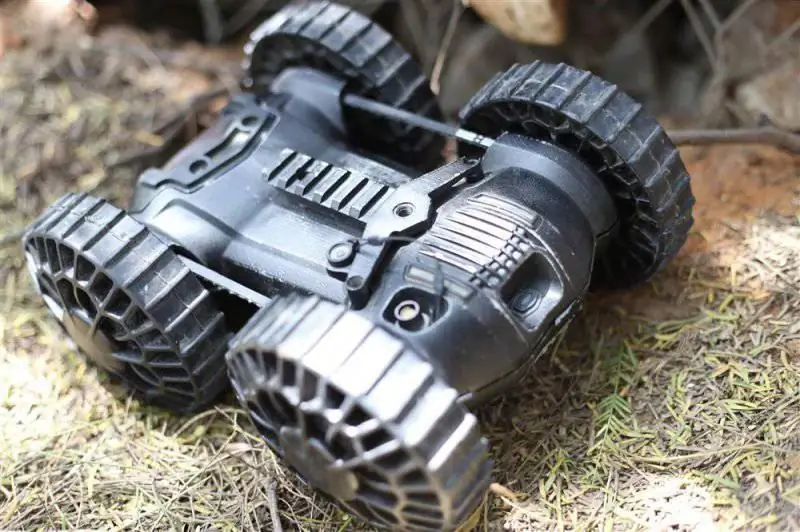


Robo-team Iris robots are equipped with a communication channel that allows you to create a self-healing network, which allows you to increase the range of these systems when working in urban conditions
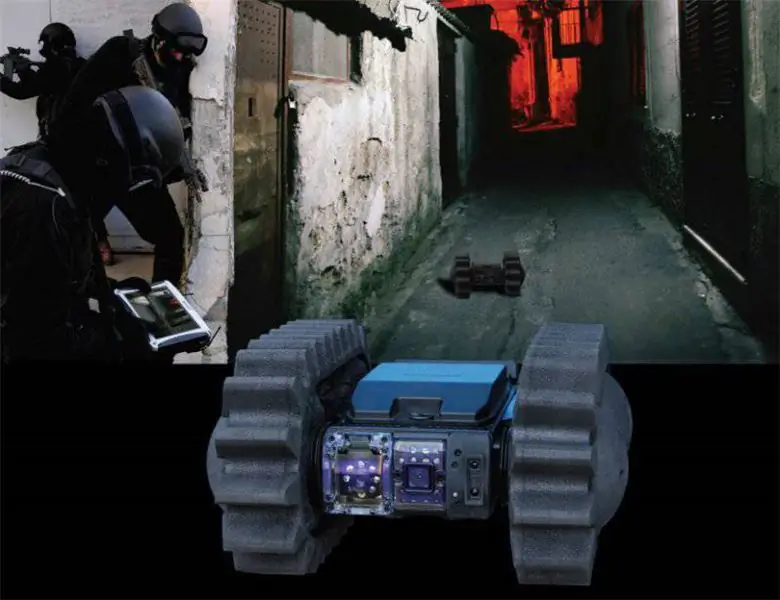

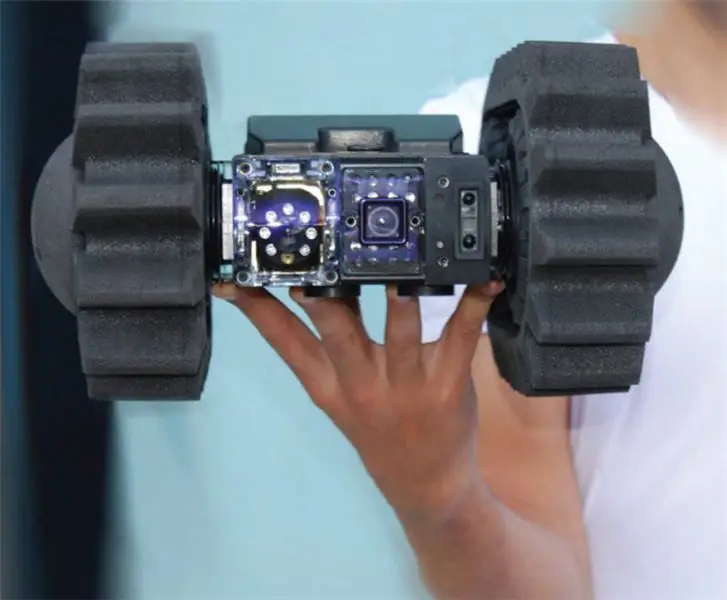
Following the acquisition of ODF Optronics by the Mistral Group, the latter is currently promoting the EyeDrive robot.
Mistral Security: In September 2013, Mistral Group acquired the Israeli company ODF Optronics and de facto entered the community of manufacturers of ground robots. EyeDrive is designed to complement the first throwable sensor created by ODF; The 4x4 configuration can be quickly converted into a tracked arrangement by adding rubber tracks to the existing wheels with a slight increase in dimensions to 350x320x165 mm.
EyeDrive weighs 3, 76 kg, each side is fitted with a black and white camera at 0.08 lux or a color camera at 0.19 lux. An optional camera with laser pointer can be mounted on the front right. It can swivel right-left by 48 °, visibility to the right is slightly reduced when the tracks are installed. A microphone capable of picking up sound from five meters is also part of the sensor kit. A one-kilogram communication module that connects via USB to a rugged laptop provides a link to the EyeDrive robot. The declared range is 400 meters in open space and 70 meters inside buildings; the robot's control signals are sent over the 915 MHz channel, while the video images are transmitted over the 2.4 GHz frequency. Lithium-ion batteries provide an average runtime of two hours (time varies depending on the sensors used), with a maximum payload of 3.5 kg. As a rule, Israeli companies are silent about their foreign customers, but it is clear that the EyeDrive robot is in service with the Israeli army.

The addition of a handle makes it easy to cast the EyeDrive or carry it around for a dog.
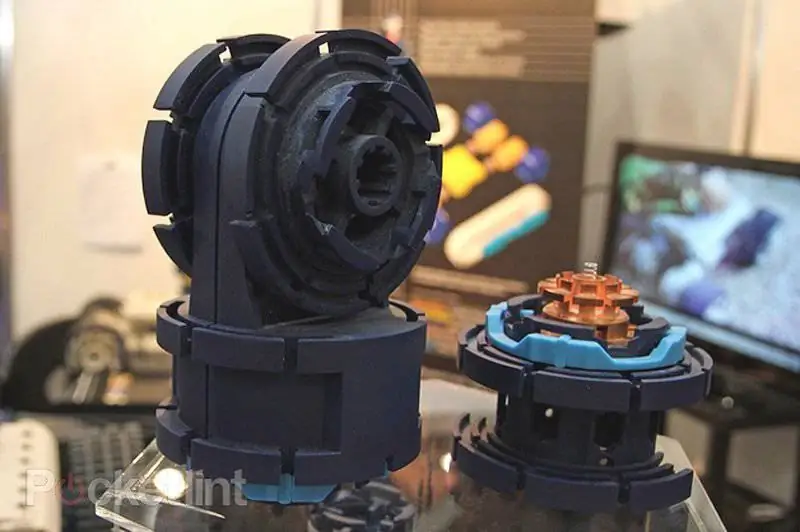
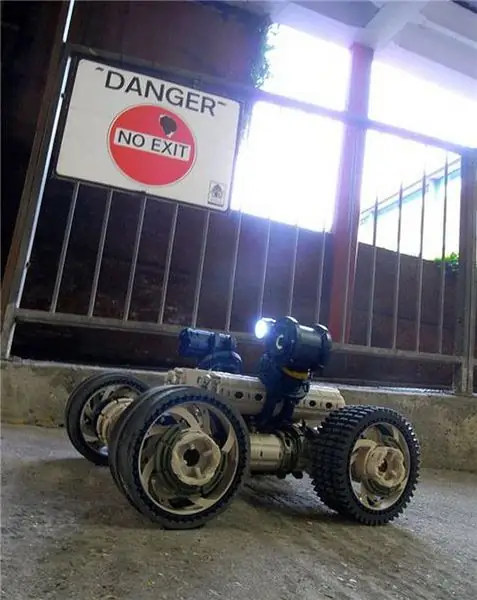
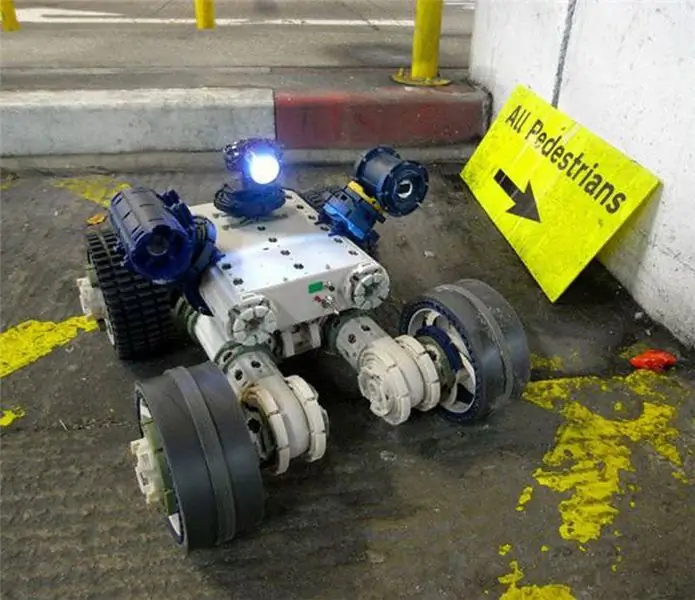



The British company Robosynthesis has developed a fully modular concept. The top photo shows the Robocube component on which most of the company's robots are based.
Robosynthesis: Categorizing ground robots is not an easy task. With Robosynthesis, this becomes even more difficult as the British company has developed a fully modular concept that allows it to reconfigure the size, configuration and role of its robots. Plug-and-play (principle of automatic recognition and configuration of connected devices) is a keyword in the Robosynthesis system. The modules, called Robocube, are the key elements of the system, since they not only allow performing specific tasks, but also have their own computing power. The patented non-metallic twist-lock universal connector provides reliable mechanical connection of modules, connection of a power supply, and a high-throughput communication channel. Various modules, be they travel modules, sensor modules, power modules, computational modules, lidars, communication modules, instrument modules, all of them are assembled into a single robot in the Lego style due to a universal connector. This same system is used to install third-party devices. Currently, the universal connector has been modified to increase the IP rating, which is equivalent to a submersion of 100 meters; this will enable Robosynthesis robots to operate in potentially explosive environments.
A design review is underway to allow modifications to be made to make the connector truly safe and ATEX certified (EU directives for equipment and operation in a potentially explosive atmosphere). With regard to mobility, several wheel models have been developed so that the robot can move around any type of terrain. To optimize mobility, Robosynthesis drew inspiration from living creatures: the hemispherical wheels for checking sewers and waterways were taken from arthropods, which use a rowing gait to avoid getting stuck on rocks or in vegetation, while the "claw" wheels imitate the work of insect legs and are used for driving over all types of terrain. Driven tracks, usually not in contact with the ground, make rolling over obstacles an advantage.
Robosynthesis robots use high-tech materials and technologies taken from Formula 1, such as metallized polymers. They are much lighter than those made from standard materials, which allows them to have a higher load capacity or a much longer run time with the same set of batteries.
Among the small robots offered by Robosynthesis, we see Armourdillo. It is a portable, drop-down tactical intelligence gathering device that can be assembled around a Robocube engine module without tools in a matter of minutes. The robot provides a 360 ° view, and its communication system can form a mesh network to increase the range and increase functional flexibility through the use of multiple Armourdillo robots. The robot is very robust and can be started with a detachable rear arm. This lever is also used to improve stability and flotation over obstacles. Driven tracks can also help in overcoming obstacles, and wheels are "claws" in off-road terrain. Four universal connectors are protected by removable covers, two on the top, one at the front and one at the back; they allow you to accept various devices with a total weight of up to two kilograms, but then the robot cannot be thrown.
Another Robosynthesis product that can be attributed to the "light" category is Roboforce 1, in a 4x4 configuration its mass is 2, 9; two connectors at the top allow you to accept two different devices (maximum weight 2.5 kg). One connector can be used to install a second power supply module, which doubles the runtime from one and a half to three hours. The protection index of the robot corresponds to IP 67, that is, it can be immersed one meter; it is equipped with a Super OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) communication link, providing a maximum throughput and range of 1000 meters in open areas and approximately 100 meters in urban buildings with indirect visibility. Roboforce 1 has a front camera on board, but various types of sensors can also be installed, including day cameras or thermal imagers. The robot can move at a speed of 4, 8 or 10 km / h.
The robots currently under development, Armourdillo and Roboforce 1, are just two of the many ground robots that can be “assembled” using Robosynthesis technology; among several projects under development, there is also an amphibious platform.
Piap: This Polish company has developed the Taktyczny Robot Miotany (TRM) tactical throwing robot. The cylindrical housing houses the electric motors and electronics (including the camera, LED headlights and microphone). Rear stabilizing tail with a weight at the end allows for proper movement. The mass of the device is 1.4 kg, it can be thrown 15-20 meters, and it can survive when it falls from a height of 9 meters. TRM dimensions are 210x167x190 mm, it can reach speeds of more than three km / h, and the duration of continuous operation is one hour. Its control station allows working with three robots at once, the transport container can accommodate three TRM robots and one control station. According to some sources, Piap is further developing its TRM and a new version of this robot is coming soon.
MacroUSA: It's not just the army that needs robots. Each year, the US Navy and Marine Corps conduct thousands of so-called Maritime Interdiction Operations (MIOs), with VBSS (Detection and Detention of Ships Conducting Illegal Maritime Activity) teams conducting search operations that often take place in hostile environments. Thus, in 2011, the Space and Naval Systems Center assessed several small drop robots and sensors at the customer's site in order to validate the requirements and develop key performance parameters for the MIO robot. MacroUSA was then awarded a contract to design and develop two experimental systems, each consisting of one display control unit and two small floating Stingray robots. The development center requested a robot weighing approximately 1.5 kg, which would fit into a Molle standard pocket (Modular Lightweight Load Carrying Equipment). In terms of mobility, it must overcome common deck obstacles such as ropes, cables, anchor chains with heights ranging from 37.7 to 50mm, and must not get stuck in deck gratings. Often the decks of ships are covered with oil and mud and therefore the robot needs sufficient grip to stay in place in these situations and to be stable in rough seas of up to 5 on traditional dhow sailboats that are common in the Red Sea and Indian Ocean. The robot must withstand a fall from five meters onto a steel deck and be waterproof to a depth of one meter, while it must not only stay on the water, but also swim, for this a float device is attached to it.
Also requested were optoelectronic sensors with the ability to work around the clock and a bi-directional audio system. A remotely controlled strobe device capable of capturing the attention of opponents or dazzling them in total darkness was also on the list. It also included attachment points for the telescopic mast and rope, plus one control unit for two robots, one controlled by the operator, and the second acting as a motion sensor to provide the rear for the entire VBSS group.
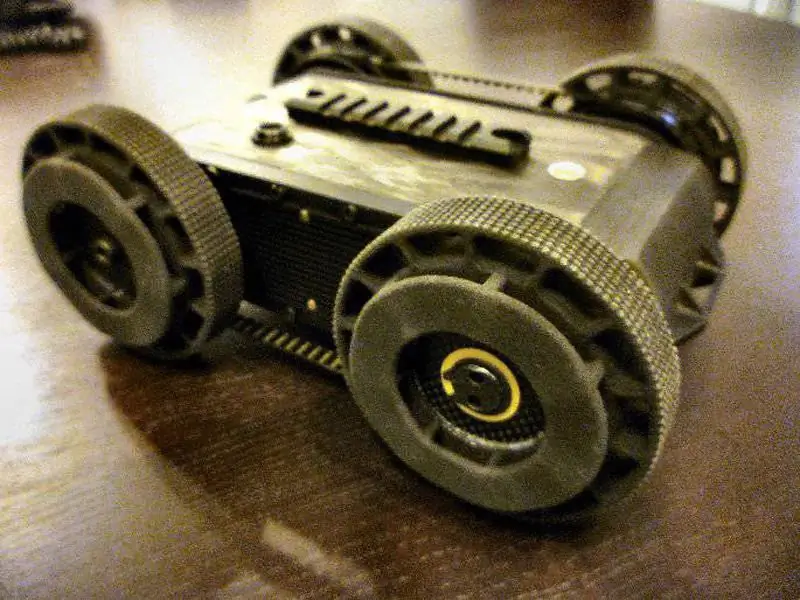
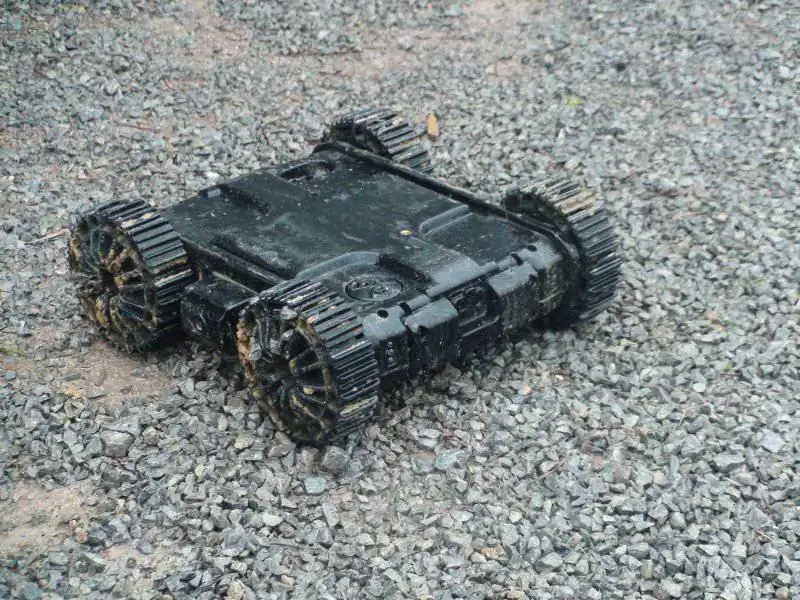


MacroUSA's Stingray is a further development of the Beetle robot, specifically designed in response to the Navy's Space and Naval Systems Command's need for a robot for maritime interdiction operations.
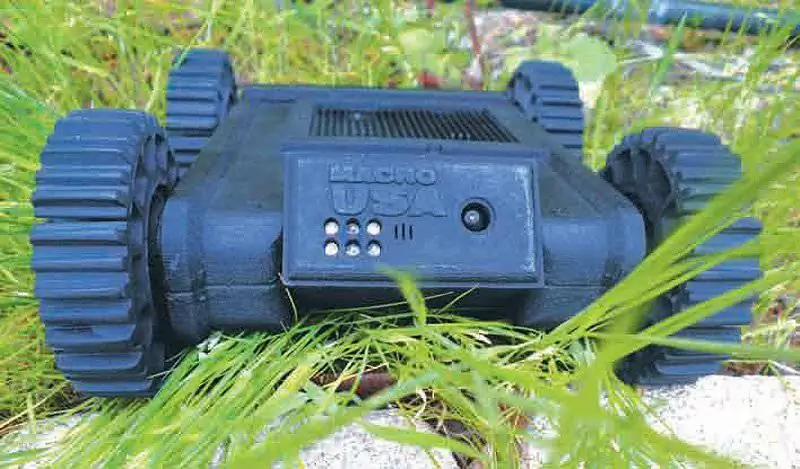

The newest version of the Beetle weighing 1.8 kg can withstand a fall from a height of three meters onto concrete and has a payload of 700 grams
For several years, the MacroUSA company catalog has already included the Beetle robot, which was suitable in size and weight, but did not meet many other requirements. One of these requirements was increased strength, the aluminum components of the Beetle were not strong enough. Cost and machining issues played not in favor of titanium, but in favor of a monolithic carbon fiber chassis with aircraft-grade aluminum sidewalls, wheels and internal brackets made of carbon fiber, closed-cell foam for buoyancy, which kept the mass within 1, 8 kg. The height is determined by the ability to overcome obstacles (to overcome a rope of 50 mm, a wheel of almost double diameter is needed), the width is determined by the battery pack; the length of the sealed landing gear of the necessary buoyancy had to be determined by the designers. Thus, the dimensions of the Stingray were 253, 9x205, 5x95, 5 mm, which is a volume of almost 4500 cm3 - this limit was set by the customer. MacroUSA soon abandoned active buoyancy systems and introduced a high visibility buoyancy device that wraps around the Stingray to operate in the water and maintains the robot's ground clearance.
Mobility in water or traction on wet or oily metal surfaces resulted in a compromise in wheel configuration. The final solution was a design with micro-tubercles on wheels and lateral protrusions with directional blades.
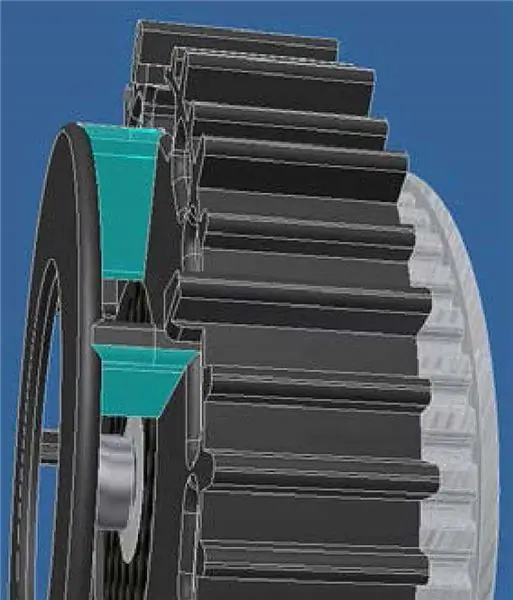
Close-up of a Stingray robot wheel with directional paddle side ridges (turquoise color)
An intermediate belt between the two axles helps to overcome obstacles. The Stingray robot is equipped with a day / night camera with a 50 ° field of view, which has tilt angles of ± 85 °; video and control signals are automatically inverted when the robot is turned over. At the front of the Stingray, white and infrared LED lights are integrated. An additional device (maximum 700 grams) can be installed on the Picatinny rail, which is connected to the robot via the RS232 connector. In this case, it is no longer recommended to throw the robot. The rechargeable batteries provide a runtime of more than two hours. There are two data transmission channels: Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing of the coded signals provides video communication, while the robot is controlled via a wideband frequency hopping signal channel. Line-of-sight range is 200 meters and in other cases 50 meters. As noted, the Stingray is an evolution of the previous Beetle, which remains in the MacroUSA catalog for customers who do not require a marine application of the robot.
With the military increasingly involved in anti-piracy operations, the company is currently awaiting a contract from the Navy's Space and Naval Systems Command (RFQ for 200 systems has already been issued).
In the top tier of the light robots category, MacroUSA developed the Armadillo, which was offered in several variants. Robots of the Armadillo V3.5 and V4.0 versions with a mass of 3, 13 kg and 3, 70 kg, respectively, remain in the throwable category, since both are able to withstand a fall from a height of 2.5 meters or a horizontal flight of eight meters. They can immediately start working after casting, since they have an absolutely symmetrical design, of course, in this case, the installation of any additional devices is not recommended. Both options are equipped with Picatinny rails and RS-232/485 connectors for installing or connecting sensors or actuators, such as explosive ordnance disposal devices, manipulators or rotary uncooled thermal imaging cameras, with a total weight of up to three kilograms. Both options have a 360 ° circular field of view provided by day / night color cameras with x2 digital zoom mounted on all sides. The front camera can tilt on V4.0 variant. The rest of the differences are minor: the V3.5 variant has two cameras, front and rear infrared LED lights, while the V4.0 has a single front camera and visible and infrared LED lights directed to all four directions. Both robots are equipped with a microphone and optional GPS system, as well as a digital accelerometer. MacroUSA uses a COFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Coded Signal Division) data link operating on the 1, 2-1, 4 or 2, 2-2, 4 GHz frequency bands (many other bands are available as an option for military customers), having a radius of action in line of sight of 300 meters and in indirect visibility of 200 meters. Armadillo robots can climb 45 ° inclines with their 130mm rubber wheels. They can be fitted with a step-climbing kit that includes flippers and rubber tracks instead of wheels. The next variant, V4.5, was designed to offer higher speeds and higher payloads. It has more connectors for connecting various devices and has been specially designed for the disposal of explosives. He takes the starting position during any coups and is able to overcome the steps.
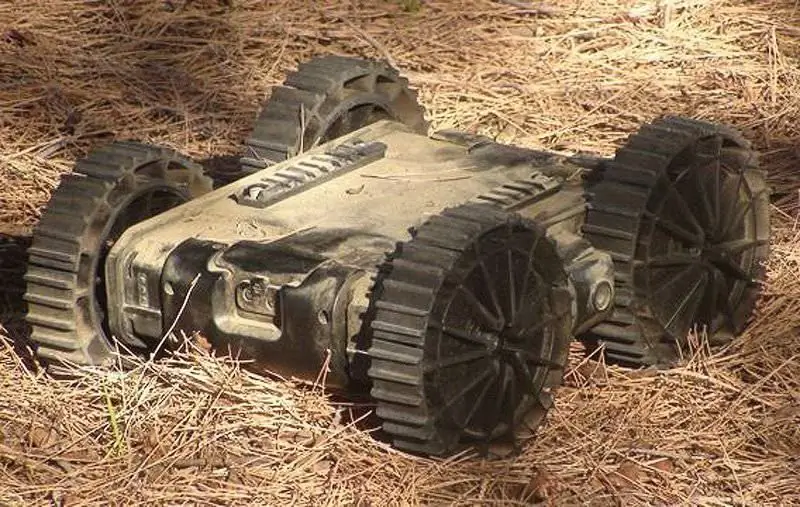

The Armadillo robot from MacroUSA is designed in different versions and can survive a fall from a height of 2.5 meters. The robot was used by other manufacturers of their own robots as a base component
Since many American programs have been closed, MacroUSA is now counting on export supplies and non-military use. The company is showing increased interest in some of its purchasing programs in Europe, France and Poland, as well as in the Far East.
The Armadillo V3.5 is the benchmark for Oto Melara's TRP3 robot. The basic robot has been thoroughly redesigned, for example, in an Italian company, the original electric motors have been replaced by brushless motors. The data transmission channel has also been improved, while the portable control unit has been modified to meet the needs of the Italian army. The stationary control box installed in the Freccia 8x8, on the other hand, was built from scratch by Oto Melara. The new control unit is based on a hardened computer with a 13-inch display, which is connected to a communication center with an integrated data link. From the very beginning, the block was created to control other ground robots developed by the company as part of the Forza NEC Italian army digitization program. When operated from a handheld device, the TRP-3 NEC robot (as it is known) gains access to the Forza NEC network via a soldier's PSTR. When controlled from the machine, the onboard programmable radio station is used to operate the robot. According to Oto Melara, the control channel has a range of 450 meters in open areas and 200 meters in urban areas. The robot was qualified by the Italian Ministry of Defense and the first batch of six robots is supplied to the Italian army.
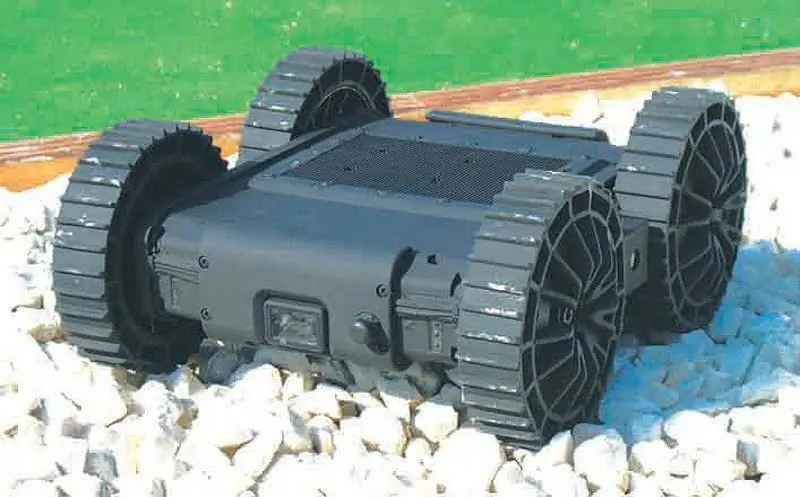

Oto Melara's TRP3 robot has been adopted by the Italian army as part of its Forza NEC digitization program
The TRP-3 NEC robot will be the "perfect eye" for medium infantry regiments equipped with a variant of the Freccia BMP. NEC's TRP-3 is slightly lighter than the original V3.5, but its dimensions are basically the same. The maximum speed is 1.8 km / h; The robot has six cameras: one daytime color camera and one nighttime camera in front, daytime cameras on the back and sides, and the sixth is installed on top of the robot to conduct inspections under suspicious cars. The Picatinny rail was integrated at the request of the customer in order to install a laser rangefinder, which, with its integrated GPS and digital compass, allows NEC's TRP-3 to obtain the coordinates of a potential target. The interface allows you to accept other types of devices.
iRobot: Among the company's products for military tasks, the 110 FirstLook robot is the smallest. The tracked, castable, self-leveling platform can withstand drops to concrete from a height of almost five meters. Without on-board equipment, the weight is 2.4 kg, the 110 FirstLook robot develops a speed of 5.5 km / h, its rubber tracks guarantee good cross-country ability on most surfaces. The device can withstand immersion up to one meter, it is equipped with two flippers for overcoming obstacles and steps. Initially, flippers were flat, but at the high temperatures encountered by the US Army and Marines in Iraq and Afghanistan, they tended to deform and were therefore replaced by more durable 3D flippers. The control unit resembles a game console in order to make it intuitive for young soldiers. The hardened waterproof control panels have a five-inch screen with a resolution of 800x480 and a weight of 0.9 kg. A 4 GHz data link (a 4.9 GHz solution is also available) offers a line-of-sight range of 200 meters. For other conditions, iRobot has specially developed radio equipment that allows the establishment of a multi-node network between robots. Originally designed to be mounted on robots, this equipment has now been redesigned as a drop-down option.
The standard kit for the 110 FirstLook is four visible / infrared cameras (hence infrared illumination on all sides) with x8 digital zoom. However, for reconnaissance tasks, other devices can be installed on the optional Picatinny rail and in the additional connector. The company has developed its own 400-gram Idac (Integrated Deployment and Camera) reconnaissance kit, which is a 270 ° mast-mounted camera that extends to a height of 155mm.
FirstLook also supports a variety of weapons of mass destruction intelligence sensors such as LCD 3.3 from Smiths Detections, MultiRAE from RAE Systems and Radiac from Canberra. The 110 FirstLook robot is not subject to the International Arms Trade Regulations and is in service with the US Army and Marine Corps and is expanding its overseas customer base.
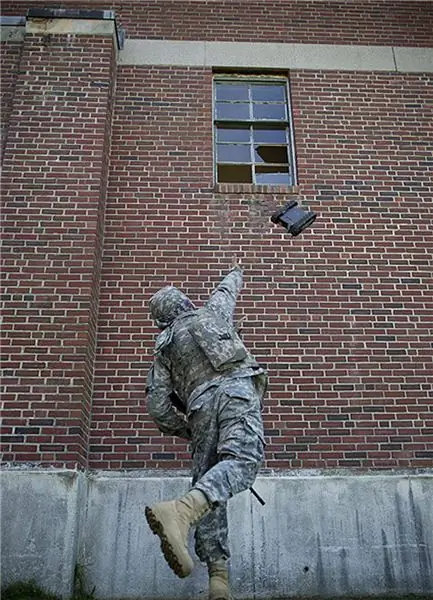

With a mass of 2.4 kg, the FirstLook device can be thrown at a long distance, and its kinetic energy is enough to break a window and get inside
Qinetiq: At the top of the weight limit for minibots is the Dragon Runner 10 from Qinetiq North America; it is the smallest member of the Dragon Runner (DR) family. The chassis can be either wheeled or tracked; changing from one configuration to another is a simple and quick operation that is carried out without special tools, the wheels are changed to drive sprockets and vice versa. The maximum speed is 6.4 km / h thanks to the non-expandable number of electric motors, which also allow you to overcome inclines up to 100% (45 °). The slim body is 50 mm from the ground, an essential performance when working in difficult terrain. If no devices are installed, then the DR10 is completely symmetrical and can start working immediately after the throw.
The operator can control the robot thanks to the front and rear day / night cameras, sounds are transmitted by the onboard microphone. The DR10 can be used with all QinetiQ control consoles. The operator sees not only the image from the cameras, but also the direction of movement and the position of the robot thanks to the built-in digital compass and GPS. Line-of-sight range is over 650 meters. Depending on the task and onboard equipment, the duration of the work varies from two to three hours. DR10 is in service with US military and foreign customers, including the UK.
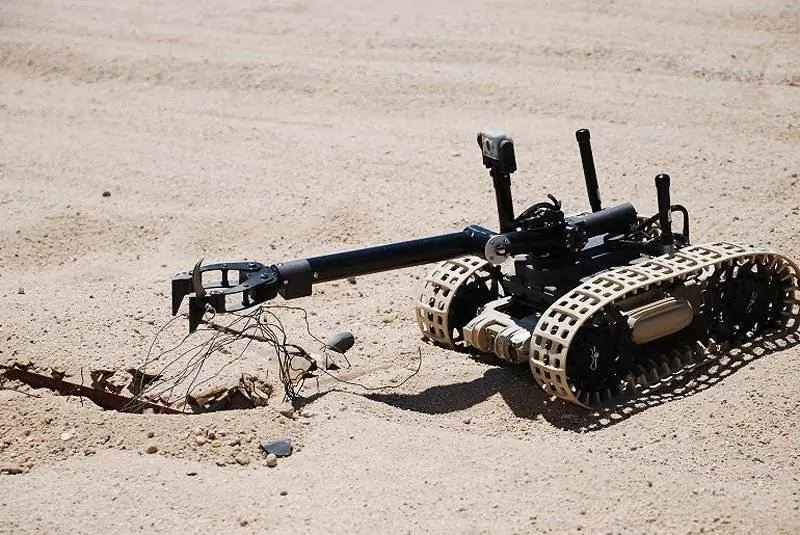
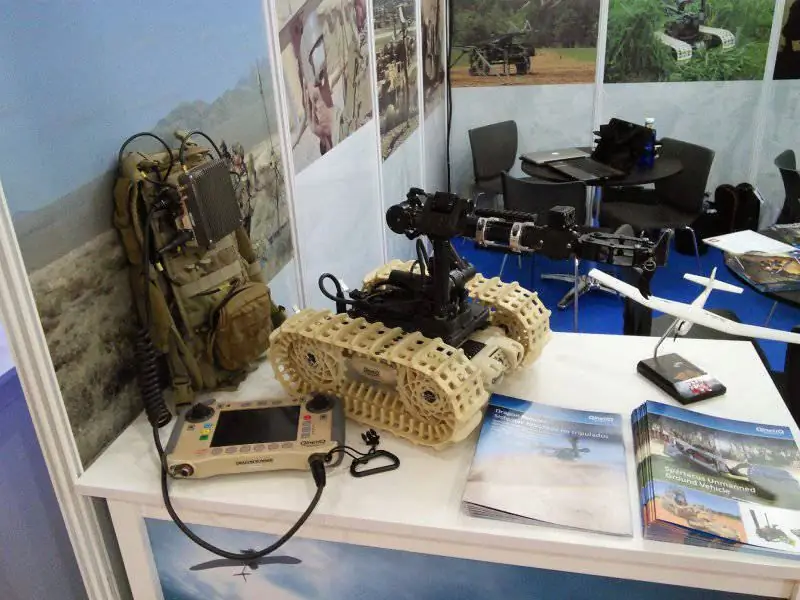


The lightest member of the Dragon Runner family, the Qinetiq DR10 robot is available in both wheeled and tracked configurations and, in the absence of additional devices, is fully symmetrical and can be deployed by throwing
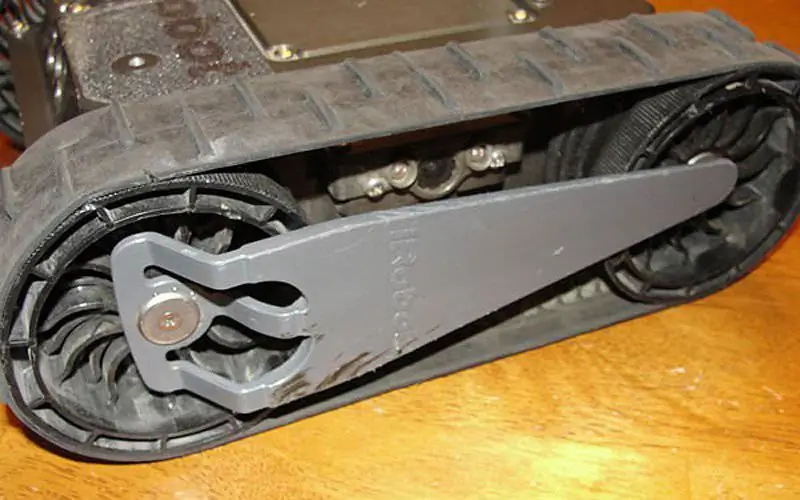


IRobot's latest FistLook configuration features new 3D flippers that are more durable, especially when working at high temperatures






